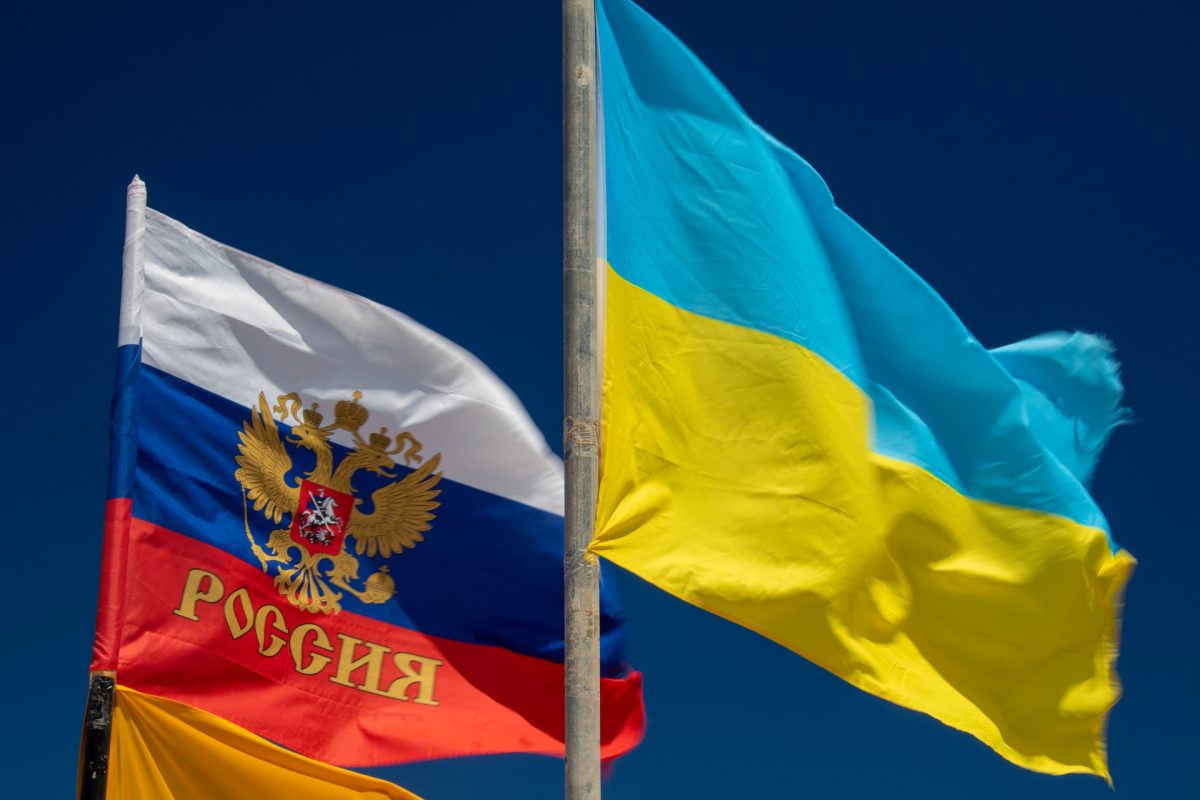
The Ukrainian-Russian war is in its third year since the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022, a major escalation of the war that has persisted since 2014. The war has invoked political instability between the United States and the EU, affecting NATO. Under the Biden administration, the United States gave billions of dollars to Ukraine in terms of humanitarian and military resources. However, re-elected President Donald Trump has had past conflicts with NATO policies regarding the EU defense guidelines.
During Trump’s address to the World Economic Forum in Switzerland, he stated that he is focusing on ending the war by lowering global oil prices to force Putin to negotiate ending the war with Ukraine.
“The United States has the largest amount of oil and gas of any country on Earth, and we’re going to use it… it will make the United States a manufacturing superpower and the world capital.” – President Donald Trump
The conflict between the two countries started when Russia began to occupy Crimea in late Feb. 2014. Since 1992, Ukraine has acknowledged the Republic of Crimea as an autonomous part of their county. The conflict further escalated in Feb. 2022 when Russia invaded Ukraine, mainly for economic interests concerning control of lithium deposits and their grain wealth.
Russia is starting to face economical hits because of this conflict. War, resource costs and population are not only affecting the European countries. They are also playing a large role in the decline of the Russian economy.
According to Doctor Craig Greathouse, professor and Political Science & International Affairs department head at the University of North Georgia, “There is economical damage being done to Russia. They have lost a significant amount of the population, specifically males… it’s the age that’s important, because it tends to be mostly younger males that are fighting.”
In 2020, at the height of COVID-19, economies all over the world were slowing down as a result of the pandemic. On top of war costs and internal economical struggles, Britain has since been in a recession. The United Kingdom withdrew from the EU in January 2020, titling the withdrawal Brexit. While part of the EU, the UK was not receiving economical growth.
Greathouse described the argument of Brexit as “tensions of British politics about whether we join for the economics or whether we protect our own sovereignty.”
Under the Biden administration, Greathouse explained that Brexit did not hurt British trade with America. The future of NATO and British trade “depends on what the Trump administration decides to do.”
Brexit also removed Britain from all prior trade treaties it possessed internationally and internally through the Union. The United States’ future relations between Britain and NATO policies remain unclear.
Since the restriction of energy supplies from Russia to many European countries, Germany and Britain are currently in recessions. It has not affected European trade with America or impacted the United States’ economy. In fact, the U.S. has somewhat benefited from the conflict.
“The restriction of energy in the European countries has allowed the U.S. to sell a lot more natural gas to Europe,” Greathouse said.
However, the war fostered tensions between NATO alliances. In 2020, Europeans would not pay the U.S. their required 2% GDP defense investment. Instead, they prioritized their funds on their own defenses. Under the Biden administration, the U.S. has provided $65.9 billion in military assistance to Ukraine.
Nathan Price, associate professor of Political Science & International Affairs at UNG, thought that the United States is getting an incredible deal by supplying Ukraine with weapons. While some American politicians were outraged with Biden’s large military spending, Price believed it has tremendous foreign policy benefits for the U.S. It signals a commitment to maintaining the U.S.’s NATO allies whilst encouraging the EU’s countries to cooperate with the United States.
Although France and Germany’s governments are indisposed, it does not have an effect on the EU’s trade policies. The economies of the countries within the EU are pooled, unitedly active in international trade. Domestic governments within the EU are not going to have any sort of foreign policy trade implications concerning the U.S. in relation to government dysfunction.
In Jan. 2025, Trump revoked Biden’s past executive order, raising NATO’s defense investment guidelines back up to 5%, creating conflicts with some of the European countries.
“The last time Trump was in office, NATO was very fractured,” Price said. He believed that the United States will not be withdrawn from NATO.
Price describes the future of NATO under the Trump Administration as “another 4 years of fractures.”
On Jan. 21, 2025, Trump declared a U.S. energy emergency, related to the current standing of Russia’s economy. He removed the U.S. from the Paris Climate Agreement, announcing his oil drilling goals. Trump has stated that he hopes by drilling for oil and becoming a global competitor for energy, he will have made a place for negotiation with Putin in hopes of ending the war in the near future.


























Cassidy • Jan 29, 2025 at 1:30 am
This was really informative and gave me a lot more insight to the tensions among the countries involved. Very well written!